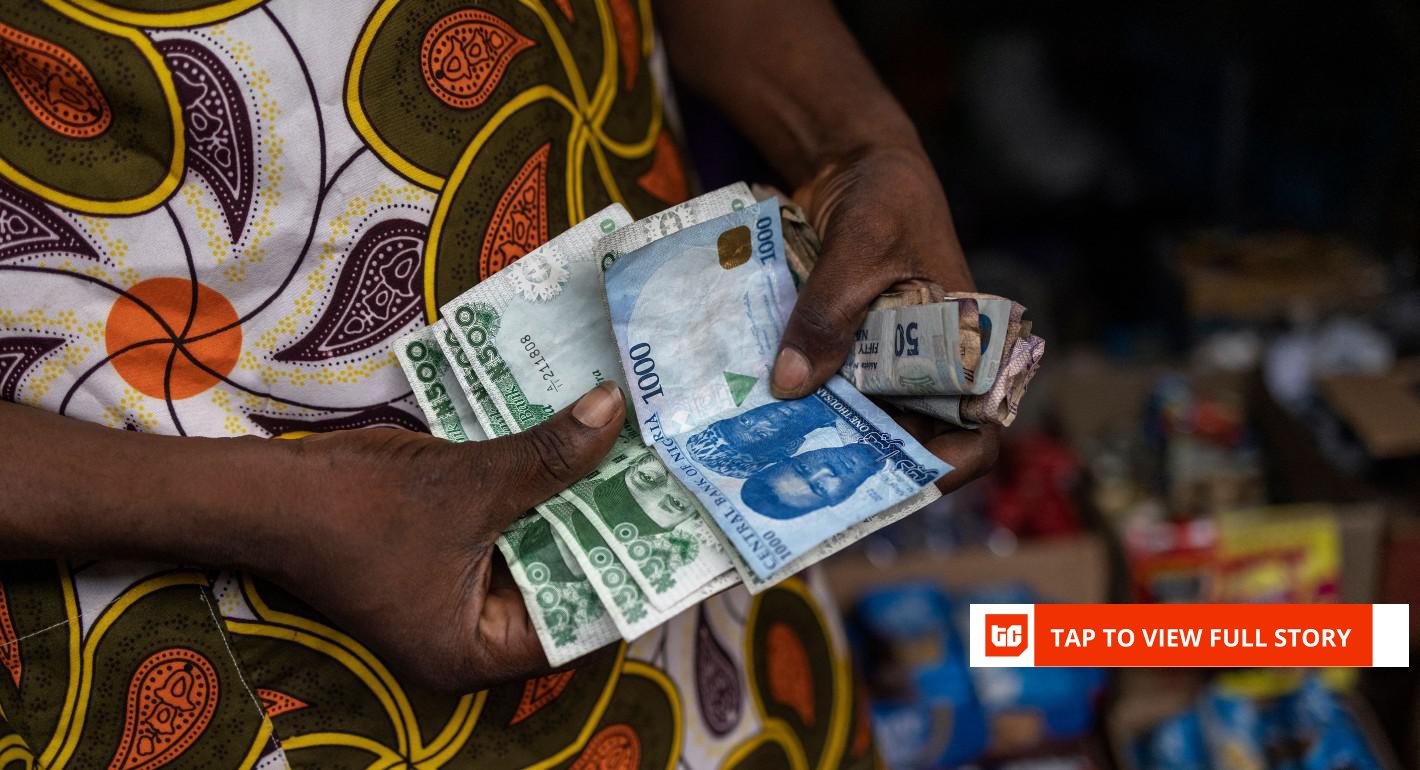
In the last decade, Nigeria has witnessed a significant decrease in cash transactions, outpacing six other cash-dependent economies. This transformation is attributed to the widespread adoption of digital payment methods and the increasing collaborations between financial institutions and fintech companies. According to a recent report by a global payment processing company, cash transactions in Nigeria dropped by 59% between 2014 and 2024, marking the most substantial decline among the seven major economies analyzed.
The shift away from cash transactions in Nigeria has been fueled by the surge in electronic payments, with projections indicating a further reduction in cash usage to 32% by 2030. The increased use of digital payments was notably accelerated in 2023 due to the Central Bank of Nigeria’s initiative to redesign the naira, aimed at discouraging cash hoarding and money laundering.
As traditional banks faced challenges in managing the sudden increase in online transactions, fintech companies like OPay and PalmPay emerged as key players, providing reliable alternatives for money transfers and bill payments amidst the cash scarcity. This transition towards non-cash transactions has been evident in the significant growth of electronic transactions in Nigeria, which surged by 16-fold between 2018 and 2024, reaching 11.3 billion transactions.
Despite Nigeria still being considered a cash-heavy economy, the rate of cash transactions has reduced by more than half since 2019, with mobile devices playing a crucial role in this transformation. The country’s financial inclusion rate has also seen improvements, rising to 64% in 2023 from 56% in 2020, with further projections indicating a potential increase to 80% by 2026.
Analysts predict that the ongoing innovations in payment processes, driven by fintech partnerships and technological advancements, will continue to reduce reliance on cash and enhance the efficiency of financial transactions in Nigeria. As a result, Nigeria is swiftly establishing itself as a leading digital finance hub in Africa, setting a precedent for the future of financial systems on the continent.














Leave a Reply